ExpSolve: Difference between revisions
From TomWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Solvers]] | [[Category:Solvers]] | ||
==Purpose== | ==Purpose== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 6: | ||
==Calling Syntax== | ==Calling Syntax== | ||
<source lang="matlab"> | |||
Prob = expAssign( ... ); | Prob = expAssign( ... ); | ||
Result = expSolve(Prob, PriLev); or | Result = expSolve(Prob, PriLev); or | ||
Result = tomRun('expSolve', PriLev); | Result = tomRun('expSolve', PriLev); | ||
</source> | |||
== | ==Inputs== | ||
{| | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!''Prob''||Problem created with expAssign. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|''PriLev''||Print level in tomRun call. | |''PriLev''||Print level in tomRun call. | ||
|- | |- | ||
''Prob.SolverL2''||Name of solver to use. If empty, TOMLAB | |''Prob.SolverL2''||Name of solver to use. If empty, TOMLAB selects dependent on license. | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | ==Outputs== | ||
{| | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!''Result''||TOMLAB Result structure as returned by solver selected by input argument ''Solver''. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|''LS''||Statistical information about the solution. See | |''LS''||Statistical information about the solution. See [[TOMLAB Appendix B]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 34: | ||
''expSolve ''solves a '''cls '''(constrained least squares) problem for exponential fitting formulates by expAssign. The problem is solved with a suitable or given '''cls '''solver. | ''expSolve ''solves a '''cls '''(constrained least squares) problem for exponential fitting formulates by expAssign. The problem is solved with a suitable or given '''cls '''solver. | ||
The aim is to provide a quicker interface to exponential fitting, | The aim is to provide a quicker interface to exponential fitting, automating the process of setting up the problem structure and getting statistical data. | ||
==M-files Used== | ==M-files Used== | ||
| Line 78: | Line 72: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
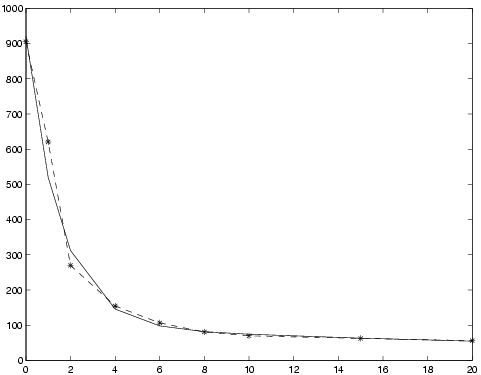
The <math> | The <math>x</math> vector contains the parameters as <math>x=[\beta_1,\beta_2,\alpha_1,\alpha_2]</math> so the solution may be visualized with | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 84: | Line 78: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<figure id="fig:expData"> | |||
[[File:Results of fitting experimental data to two-term exponential model.png|thumb|550px|none|alt=Results of fitting experimental data|<caption>Results of fitting experimental data to two-term exponential model. Solid line: final model, dash-dot: data.</caption>]] | |||
</figure> | |||
Latest revision as of 08:10, 10 January 2012
Purpose
Solve exponential fitting problems for given number of terms p.
Calling Syntax
Prob = expAssign( ... );
Result = expSolve(Prob, PriLev); or
Result = tomRun('expSolve', PriLev);Inputs
| Prob | Problem created with expAssign. |
|---|---|
| PriLev | Print level in tomRun call. |
| Prob.SolverL2 | Name of solver to use. If empty, TOMLAB selects dependent on license. |
Outputs
| Result | TOMLAB Result structure as returned by solver selected by input argument Solver. |
|---|---|
| LS | Statistical information about the solution. See TOMLAB Appendix B. |
Description
expSolve solves a cls (constrained least squares) problem for exponential fitting formulates by expAssign. The problem is solved with a suitable or given cls solver.
The aim is to provide a quicker interface to exponential fitting, automating the process of setting up the problem structure and getting statistical data.
M-files Used
GetSolver, expInit, StatLS and expAssign
Examples
Assume that the Matlab vectors t, y contain the following data:
To set up and solve the problem of fitting the data to a two-term exponential model
,
give the following commands:
>> p = 2; % Two terms
>> Name = 'Simple two-term exp fit'; % Problem name, can be anything
>> wType = 0; % No weighting
>> SepAlg = 0; % Separable problem
>> Prob = expAssign(p,Name,t,y,wType,[],SepAlg);
>> Result = tomRun('expSolve',Prob,1);
>> x = Result.x_k'
x =
0.01 0.58 72.38 851.68
The vector contains the parameters as so the solution may be visualized with
>> plot(t,y,'-*', t,x(3)*exp(-t*x(1)) + x(4)*exp(-t*x(2)) );
<figure id="fig:expData">
</figure>



![{\displaystyle x=[\beta _{1},\beta _{2},\alpha _{1},\alpha _{2}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/897935525bb63f657211784d2394653e5a683c80)